People have been manipulating the cannabis plant to amplify its properties for centuries. The most recent innovation of this kind is that of cannabis extraction. Extracts picked up major popularity alongside dab culture, and slowly but surely they have become just as prominent as flowers. As new methods emerge, extracts are being used for far more than dabbing. They have become instrumental for infusing products into edibles and topicals. Extracts are also proving valuable in the realm of scientific research and cannabis pharmaceutical developments.
A cannabis extract is defined by the method through which it’s made. While concentrates like hash and kief are made with natural methods, extracts are defined by the fact that they’re made using a solvent. There are a few types of popular solvents in the extraction industry. Butane (BHO), Carbon Dioxide (CO2), Ethanol (EHO), and even propane are viable options in cannabis extraction.
Co2 Extraction
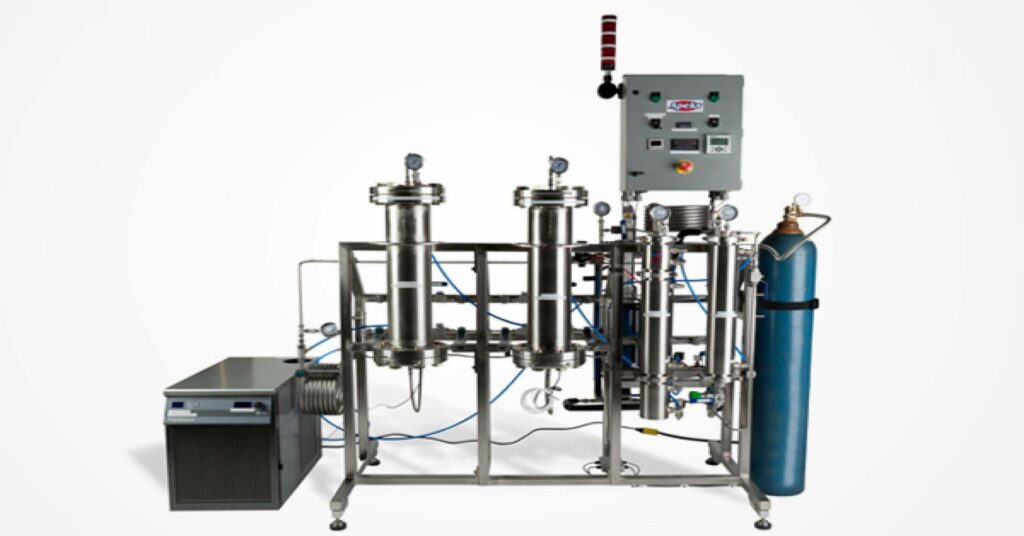

Unlike BHO, carbon dioxide (CO2) is considered safe by the FDA which has made it a more desirable solvent among extractors in the cannabis community. The solvent is also non-toxic and the process doesn’t contribute to carbon emissions in the atmosphere. This method uses a specific combination of high temperature and pressure to create phase changes in the CO2. Controlling the temperature and pressure allows us to create a multitude of end products, making CO2 a “tunable” solvent. The phase changes are used to “drop out” the undesirables from the plant material. Some CO2 machines and methods are able to extract and separate multiple compounds from the plant, but it does take a more finely tuned set of equipment and experience to harvest both terpenes and cannabinoids. This solvent has become very popular because it is both safe and highly efficient. It also works as a sanitizing agent, meaning that it prolongs shelf life provided that we are using the proper system in the right environment. These extracts tend to be more viscous, which is why they are more often found in vape cartridges than on our dab tool.
Rosin
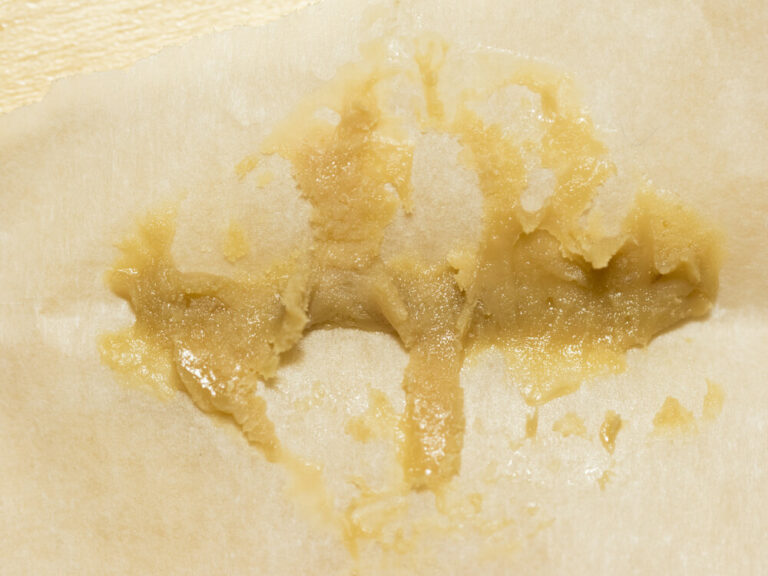
The rosin method doesn’t actually need a solvent, which makes it more attractive and also not a cannabis extraction at all. But since the end product is similar to other extracts, rosin is actually a concentrate. It is created by using heat and pressure instead of a solvent like those listed above. Without a solvent or expensive machinery to run said solvent, rosin is much less expensive to manufacture than BHO or CO2. The process to create this concentrate is also much less complicated than solvent extractions, so much so that it can be made at home.
The creators of home methods were the first to discover the gift of rosin. These methods use hair straighteners and micron bags to extract enough for the home user. With the success of homemade rosin, a few wholesale rosin machines are available for purchase, which has made rosin available for the average consumer at their local dispensary. Since it’s inception, squished concentrates have picked up serious fame in the cannabis community.
Extractions have been around for a long time in the oil, pharmaceutical, and other prominent industries.
We are currently at an exciting point in time we are watching the home taught extractors who have only worked with the cannabis plant are meeting Ph.D. chemists to create products that previous stoners have only dreamt about. These are the four most commonly available extracts that can be found at various stores today.
If you want to buy a rosin press, make sure to check out our article about the best rosin press machines available today.
DHO Extraction by Dexso
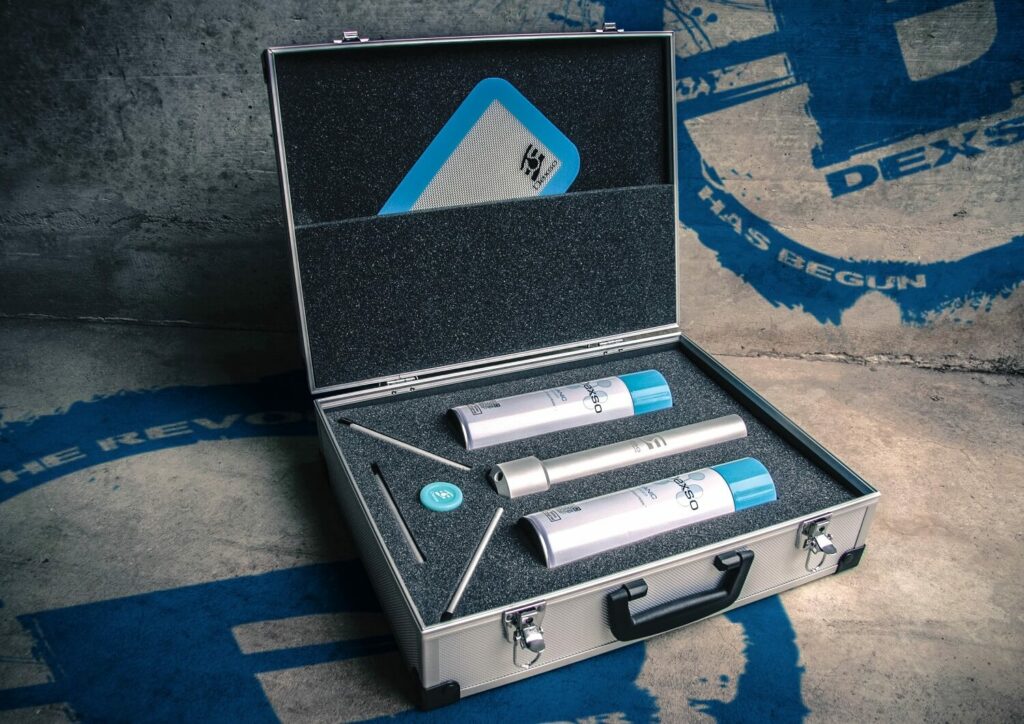

Though butane extracted cannabis wax is highly popular, the term BHO has picked up quite the stigma. Because of this, many extractors have searched for similar solvents that wouldn’t turn off the consumer quite as much. Enter Dimethyl ether, the newest solvent in the world of cannabis extractors. Wax blown using Dimethlyl ether is often called DHO and is crafted using many of the same tools used to make BHO. DHO is processed in an ecological CO2 neutral way and has been used in pharmaceutical and food grade products for years. The Swiss company Dexso has launched their gas in 2014 and their solvent is loved by many extraction artists in Europe and all over the world.
It is known in cannabis extraction as a pure and strong solvent for the job. Dimethyl ether also has a stronger extraction capacity than butane, meaning that it provides a larger yield. It also leaves very little undesirables, evaporates faster, and is less explosive than butane. These differences are made possible by the Oxygen molecule that is found in Dimethyl ether (DME) but not in butane. The process of cannabis extraction is also a bit different with DHO than BHO. Fresh, frozen materials work best for getting a large terpene content. 24-hours before extraction it is best to freeze the extractor filled with flowers, this tactic will freeze and block water which also helps reduce the amount of lipids that are picked up.
Cold is crucial in this process for a high yield with DME extraction, with the equipment, start materials, and solvent. Compression will also create a high yield, but minimal compression should be used for a higher quality extract. The extraction liquid will cool off very quickly as the DME evaporates, accelerating the condensation process which could form ice in the extract. To reduce condensation and avoid this heat the Pyrex dish we pour the extract into. If ice does form we have to be patient and wait for it to melt and purge more carefully in the post-extraction processes.
Butane Extraction
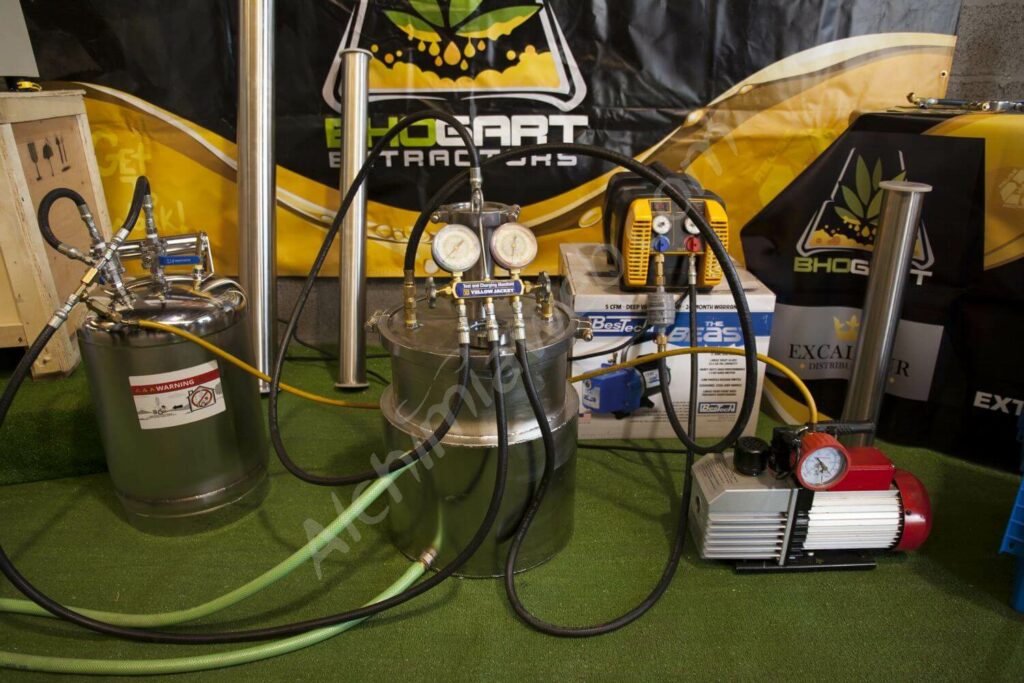

The butane extraction method is most often used to create dabbable products. BHO products often go by the name wax, shatter, snap and pull, etc. Butane is a highly volatile hydrocarbon which makes working with it outside of an extraction lab very dangerous. Despite this stigma, butane extraction is safe when pulled in a compliant, properly outfitted and ventilated laboratory.
Downstream products of butane extraction are generally referred to as BHO, which, depending on who you’re asking, stands for Butane Honey Oil or Butane Hash Oil. With BHO, essential oils are extracted from the fresh, fresh frozen, or dried and cured flowers. We learned some more about butane extraction on Skunk Pharm Research, a site originally run by JD Ellis. It is a desirable solvent for extractors because it is relatively non polar. That means the finished product excludes water soluble compounds like plant alkaloids and chlorophyll. After winterization and purging, the extract is ready to dab. But only a seasoned extractor will be able to go through the entire process without losing the terpenes.
Butane extracts are also safe to dab because a knowledgeable extractor will have purged out all of the ‘tane. It is easy to purge because it has a boiling point that is about the same temperature as when water freezes. The process of purging is often sped up by moving air over the raw extract to help the butane molecules escape through the surface of the oil. Bottom heat can also be added to inspire a faster purge, but heat may compromise a lot of the terpenes. A vacuum purge helps maintain the cannabinoids in their carboxylic acid form. A properly purged extract has been deemed safe to dab by most governing bodies. To ensure that an extract is compliant, only purchase from a brand that provides test results for residual solvents.
Ethanol Extraction
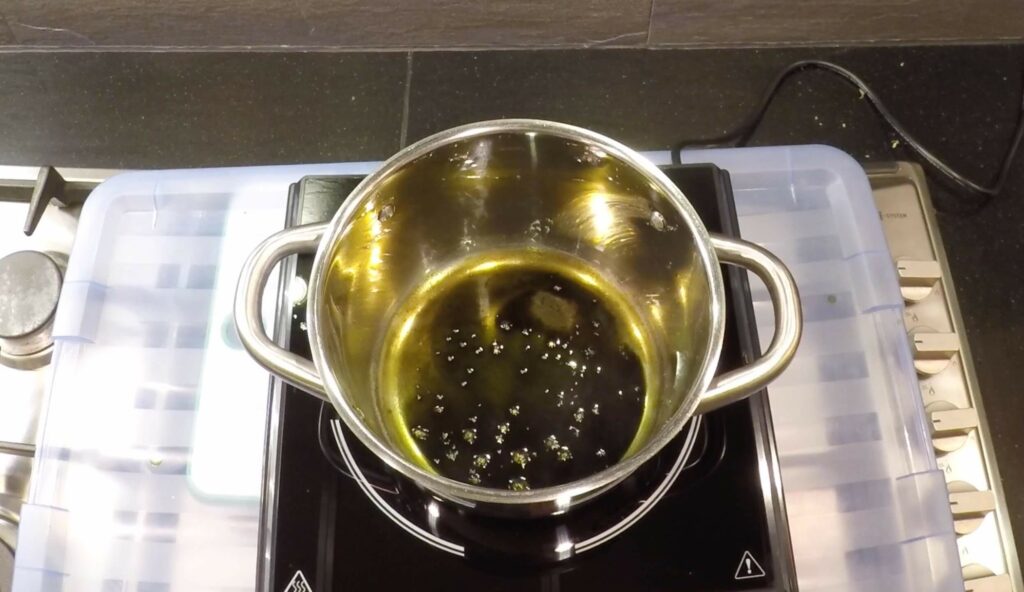

Ethanol extractions are generally ingesting as opposed to inhaled, like the popular medicine Rick Simpson Oil. Using ethanol to extract the beneficial compounds from the cannabis plant is considered much safer and far more simple than other popular methods. Crafting an ethanol extract takes about a 3-minute wash in the chosen solvent. With that information it seems to be common sense to take more time or add heat for the purpose of extracting more of the compounds, but this will also extract undesirables like chlorophyll, plant waxes, and vegetable oil. In general, Quick Wash Ethanol (QWET) will pick up a lot of these undesirables. But again, certain methods can help reduce this pick up.
Start materials taken fresh from the plant don’t work very well for QWET since it generally has higher water content. Flowers cured to about 15% water content perform best using the Skunk Pharm Research methods. Simply wash the buds, broken up by hand and decarbed in the oven, for three minutes; agitating multiple times to ensure that the herbs are fully covered. After three minutes, strain the materials in a wire mesh strainer. Do not push on the herbs, just let them drain using gravity and time. Now put the oil into a sealed jar and give it an oil bath at 250°F to filter the extracted liquid. Boil or distill off the liquid until there is no more solvent remaining or the liquid is reduced to a simple pool of oil. At this point in the process it can either be refined further or sucked up in a syringe and used as is.

Hello I suffer with back pain do you have a product that will help with my problem back